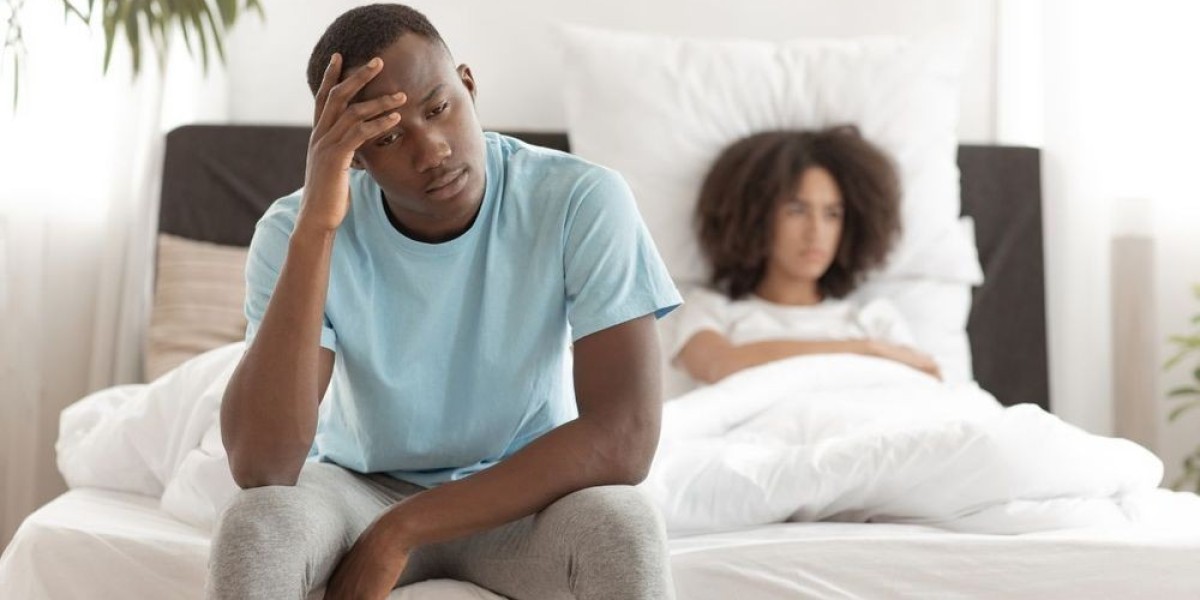
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is one of the most common sexual health issues faced by men worldwide. It is defined as the inability to achieve or maintain an erection sufficient for sexual activity. While it’s often associated with aging, ED is not an inevitable part of growing older. Its causes can be physical, psychological, or a combination of both. Identifying the root cause is essential to finding an effective treatment.
While Vidalista 80 mg can provide temporary relief, long-term success in overcoming ED often requires addressing its root causes.
Always prioritize your overall health, and if you’re considering Vidalista 40mg, consult your doctor to ensure it’s the right choice for you.
This blog explores the main causes of erectile dysfunction and how they can be addressed.
What Happens During an Erection?
To understand the causes of ED, it's essential to know how an erection occurs. It involves a complex process:
- Nervous System Activation: Sexual arousal triggers the brain to send signals to the nerves in the penis.
- Increased Blood Flow: Blood vessels relax, allowing more blood to flow into the penis.
- Retention of Blood: Muscles in the penis trap the blood, maintaining the erection.
Disruptions in any part of this process can lead to erectile dysfunction.
The Main Causes of Erectile Dysfunction
1. Physical Causes
Physical health plays a significant role in erectile function. Common physical causes include:
Cardiovascular Disease
Poor heart health can restrict blood flow to the penis, making it difficult to achieve or maintain an erection. Conditions like atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries) are a major contributor to ED.Diabetes
High blood sugar levels can damage nerves and blood vessels, impairing the mechanisms needed for an erection. Diabetes is one of the leading causes of ED, particularly in men under 50.Obesity
Excess weight is linked to reduced testosterone levels, poor blood circulation, and increased risk of diabetes—all of which can cause ED.Hormonal Imbalances
Low testosterone, also known as hypogonadism, can lead to reduced sexual desire and erectile dysfunction. Hormonal issues can also arise from conditions like thyroid disorders or the use of certain medications.Neurological Disorders
Conditions like Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis, or spinal cord injuries can interfere with the nervous system’s ability to trigger erections.Chronic Illness
Diseases like kidney failure, liver disease, or cancer can impact physical and emotional health, leading to ED.Medications and Substance Use
Some prescription drugs, such as antidepressants, antihistamines, and blood pressure medications, can cause ED as a side effect. Excessive alcohol consumption, smoking, and recreational drug use can also impair erectile function.
2. Psychological Causes
The mind plays a crucial role in sexual function. Psychological factors that can cause ED include:
Stress and Anxiety
Work pressure, financial worries, or life challenges can distract the mind and interfere with sexual arousal. Performance anxiety—worrying about satisfying a partner—can exacerbate the issue.Depression
Depression often leads to reduced libido and difficulty achieving erections. The condition itself, as well as the medications used to treat it, can contribute to ED.Relationship Problems
Poor communication, unresolved conflicts, or lack of emotional intimacy can strain relationships and lead to ED.Trauma
Past experiences, such as sexual abuse or emotional trauma, can cause psychological barriers to sexual performance.
3. Age-Related Factors
While ED is not an inevitable part of aging, the risk increases with age. This is often due to:
- Reduced Testosterone Levels: Testosterone naturally declines after the age of 30, affecting libido and erectile function.
- Cumulative Health Issues: Older men are more likely to develop conditions like heart disease, diabetes, or high blood pressure, which contribute to ED.
Identifying the Root Cause of ED
To determine the cause of ED, healthcare professionals may perform:
- Physical Exams: Checking for underlying health issues, such as high blood pressure or obesity.
- Blood Tests: Assessing testosterone levels, blood sugar, and cholesterol.
- Psychological Evaluation: Exploring emotional or psychological factors contributing to ED.
- Other Tests: Ultrasounds or nocturnal penile tumescence tests to evaluate blood flow and erections during sleep.
Addressing the Main Causes of ED
1. Treating Physical Health Conditions
- Managing chronic conditions like diabetes or high blood pressure can improve ED.
- Medications like sildenafil (Viagra), tadalafil (Cialis), or vardenafil (Levitra) can help by increasing blood flow to the penis.
2. Lifestyle Changes
- Quit smoking and reduce alcohol consumption.
- Exercise regularly to improve cardiovascular health and circulation.
- Maintain a balanced diet to support overall health.
3. Psychological Support
- Therapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), can address anxiety, depression, or trauma.
- Couples counseling can improve communication and intimacy.
4. Hormonal Therapy
Testosterone replacement therapy may be an option for men with low testosterone levels.
Preventing Erectile Dysfunction
While not all causes of ED are preventable, adopting a healthy lifestyle can reduce the risk:
- Exercise regularly to maintain good circulation and healthy weight.
- Eat a heart-healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Manage stress through mindfulness, meditation, or relaxation techniques.
- Avoid smoking and limit alcohol consumption.
Conclusion
Erectile dysfunction can stem from a variety of physical and psychological causes. Understanding the root cause is the first step toward effective treatment. Whether it's addressing chronic conditions, making lifestyle changes, or seeking psychological support, there are numerous strategies to regain sexual health and confidence.