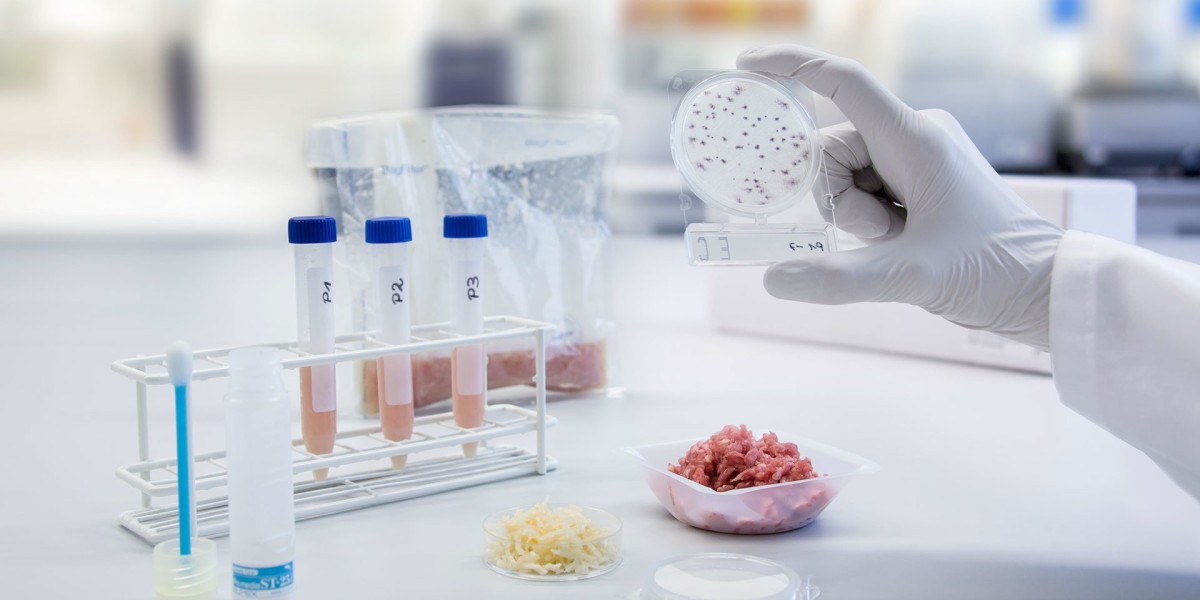
Microbiological tests are critical tools in medicine, food safety, environmental monitoring, and pharmaceutical industries. They involve the study and analysis of microorganisms like bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites to detect infections, assess contamination, and ensure overall safety.
What Are Microbiological Tests?
Microbiological tests involve the identification and analysis of microorganisms to detect infections, evaluate contamination levels, or assess product safety. These tests are widely used in various fields such as:
- Healthcare: Diagnosing infections and guiding treatment plans.
- Food Industry: Ensuring food safety by detecting harmful pathogens.
- Pharmaceuticals: Monitoring sterile environments and product quality.
- Environmental Studies: Assessing water, soil, and air quality.
Importance of Microbiological Tests
Microbiological tests play a vital role in ensuring public health, environmental safety, and industrial compliance. Here’s why they are essential:
1. Early Disease Detection
In healthcare, microbiological tests help diagnose infections caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites. Early detection allows for timely treatment, improving patient outcomes.
2. Preventing Outbreaks
Regular testing in food production and water systems prevents the spread of harmful pathogens, reducing the risk of outbreaks.
3. Quality Control
In industries like pharmaceuticals and cosmetics, microbiological tests ensure products meet safety and quality standards.
4. Environmental Monitoring
These tests help monitor environmental contamination, ensuring ecosystems remain balanced and safe.
Types of Microbiological Tests
Microbiological tests vary depending on the purpose and the type of microorganisms being studied. Here are the most common types:
1. Bacterial Culture Tests
- Purpose: Identify bacterial infections by growing bacteria in a controlled environment.
- Applications: Diagnosing urinary tract infections, respiratory infections, and wound infections.
2. Viral Tests
- Purpose: Detect the presence of viruses using techniques like PCR (polymerase chain reaction).
- Applications: Diagnosing viral diseases such as influenza, COVID-19, and hepatitis.
3. Fungal Tests
- Purpose: Identify fungal infections through culture or molecular techniques.
- Applications: Diagnosing conditions like athlete’s foot, ringworm, and systemic fungal infections.
4. Parasitological Tests
- Purpose: Detect parasites in blood, stool, or other samples.
- Applications: Diagnosing malaria, giardiasis, and other parasitic infections.
5. Antibiotic Sensitivity Tests
- Purpose: Determine the effectiveness of antibiotics against specific bacteria.
- Applications: Guiding appropriate antibiotic therapy.
6. Endotoxin Testing
- Purpose: Detect endotoxins in pharmaceuticals and medical devices.
- Applications: Ensuring product safety in healthcare and industry.
7. Environmental Microbiology Tests
- Purpose: Assess microbial contamination in air, water, and soil.
- Applications: Monitoring environmental health and compliance with regulations.
8. Rapid Diagnostic Tests (RDTs)
- Purpose: Provide quick results for infections like malaria or strep throat.
- Applications: Point-of-care testing in clinics and hospitals.
How Microbiological Tests Are Performed
The procedures for microbiological tests can vary depending on the type of test. Here’s an overview of the general steps:
1. Sample Collection
- Sources: Samples can include blood, urine, stool, tissue, water, food, or environmental swabs.
- Procedure: Use sterile containers and follow proper techniques to avoid contamination.
2. Laboratory Processing
- Step 1: Samples are transported to the lab under controlled conditions.
- Step 2: Technicians prepare the samples for analysis, which may include culturing, staining, or molecular techniques.
3. Analysis
- Techniques Used:
- Microscopy: Observing microorganisms directly under a microscope.
- Culture Methods: Growing microorganisms on agar plates or in liquid media.
- Molecular Methods: Techniques like PCR for genetic analysis.
- Biochemical Tests: Identifying microbial properties through chemical reactions.
4. Reporting Results
- Results are interpreted by specialists and shared with healthcare providers or industry professionals for further action.
Applications of Microbiological Tests
Microbiological tests are used across various sectors, each with unique applications:
1. Healthcare
- Diagnosing infections like pneumonia, tuberculosis, and meningitis.
- Monitoring the effectiveness of antimicrobial treatments.
2. Food and Beverage Industry
- Detecting pathogens like Salmonella, E. coli, and Listeria.
- Ensuring hygiene and safety in food production.
3. Pharmaceutical Industry
- Conducting sterility tests on medications and medical devices.
- Detecting contaminants to ensure product safety.
4. Environmental Studies
- Testing water quality for pathogens or harmful bacteria.
- Monitoring soil and air for microbial contamination.
5. Research and Development
- Studying microbial behavior, resistance, and genetics.
- Developing new drugs, vaccines, and diagnostic tools.
Benefits of Microbiological Tests
Microbiological tests offer numerous benefits, including:
- Accurate Diagnoses: Identifying the exact cause of infections enables targeted treatments.
- Improved Public Health: Regular testing prevents disease outbreaks and ensures safety.
- Enhanced Product Safety: Industries can maintain high-quality standards.
- Environmental Protection: Monitoring contamination helps safeguard ecosystems.
Challenges in Microbiological Testing
Despite their importance, microbiological tests come with challenges:
- Time-Consuming: Culture-based methods can take days to yield results.
- Contamination Risks: Improper sample handling can lead to inaccurate outcomes.
- Cost: Advanced techniques like molecular testing can be expensive.
- Antimicrobial Resistance: Emerging resistant strains complicate testing and treatment.
Tips for Reliable Microbiological Testing
- Follow Protocols: Adhere to standardized procedures for sample collection and handling.
- Ensure Sterility: Use sterile equipment and containers to avoid contamination.
- Maintain Communication: Share detailed information with laboratory professionals to guide analysis.
- Choose Accredited Labs: Work with certified laboratories for accurate and reliable results.
Final Thoughts
Microbiological tests are indispensable for diagnosing infections, ensuring product safety, and protecting public health. Their applications span multiple industries, making them a cornerstone of modern science and medicine. Understanding the types, procedures, and benefits of these tests can help you appreciate their role in maintaining a safe and healthy environment.