Polyvinyl alcohol (PVA), or alcool polyvinylique in French, is a synthetic polymer that has a variety of important applications in numerous industries, ranging from packaging and textiles to pharmaceuticals and adhesives. Due to its versatile properties, it has become an essential material in both industrial and commercial sectors. PVA is known for being water-soluble, which gives it unique characteristics and opens the door to a range of practical uses. In this article, we will explore the chemical structure, properties, production methods, and applications of Polyvinyl Alcohol, shedding light on why it is such a valuable material.
Chemical Structure and Properties
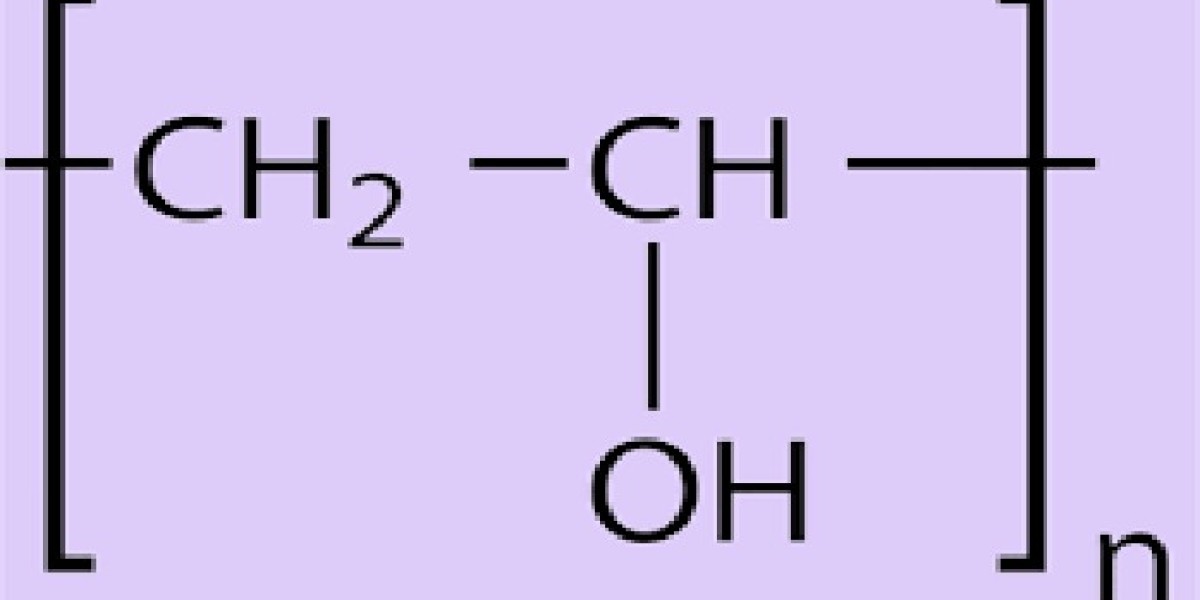
Polyvinyl alcohol is a water-soluble synthetic polymer made from the polymerization of vinyl acetate (CH3COOCH=CH2) monomers, followed by hydrolysis. The polymer’s backbone consists of carbon atoms bonded to hydrogen atoms, with hydroxyl (–OH) groups attached to the carbon chain. These hydroxyl groups are key to PVA’s solubility in water and its ability to form hydrogen bonds with other molecules, enhancing its adhesive and film-forming properties.
The polymer typically has a molecular weight ranging from 10,000 to 250,000 Daltons. The degree of hydrolysis—the extent to which the acetate groups are removed from the polymer—plays a major role in the properties of PVA. For example, a higher degree of hydrolysis leads to improved water solubility, while a lower degree of hydrolysis can result in a polymer that is less soluble but has enhanced film-forming abilities.
PVA’s most notable properties include:
- Water Solubility: It dissolves easily in water, which makes it useful for applications where water solubility is desired.
- Film-Forming: PVA is capable of forming thin, flexible films that are impermeable to oils and greases but can dissolve in water.
- Biodegradability: Unlike many synthetic polymers, PVA is biodegradable under certain conditions, making it an environmentally friendly option compared to non-biodegradable alternatives.
- Adhesive Properties: The polymer has strong adhesive properties, especially when applied in aqueous solutions.
- Non-Toxic: PVA is considered non-toxic and safe for use in many applications, including food and pharmaceutical industries.
Production Methods
The production of Polyvinyl Alcohol involves two key steps: the polymerization of vinyl acetate and the subsequent hydrolysis of the resulting polyvinyl acetate (PVAc) polymer.
- Polymerization of Vinyl Acetate: The process begins with the polymerization of vinyl acetate to form polyvinyl acetate. This is typically done through free-radical polymerization, in which vinyl acetate monomers react under the influence of an initiator such as hydrogen peroxide or azo compounds to form a polymer chain.
- Hydrolysis of Polyvinyl Acetate: The second step involves the hydrolysis of polyvinyl acetate (PVAc) to produce polyvinyl alcohol. In this process, the ester linkages (–COO–) in the polymer are broken by a reaction with water, replacing the acetate groups with hydroxyl groups (–OH). This step can be done under acidic or alkaline conditions, depending on the desired degree of hydrolysis. The extent of hydrolysis determines the final properties of the PVA, such as water solubility and strength.
Both of these steps are crucial in controlling the characteristics of the final product, such as its molecular weight, solubility, and mechanical properties. The production process must be carefully controlled to achieve the desired balance between these properties for specific applications.
Applications of Polyvinyl Alcohol
Polyvinyl Alcohol is an extremely versatile polymer with applications in many different industries. Some of the most common uses of PVA include:
- Packaging and Films
One of the most common applications of PVA is in the production of water-soluble films. These films are used for packaging products such as detergents, pharmaceuticals, and food items. Water-soluble PVA films are convenient for single-use applications, as they can dissolve completely in water, reducing waste. These films are often used in laundry detergent pods, where the packaging dissolves in the wash cycle, releasing the detergent without requiring the user to open the package.
- Adhesives
PVA is widely used as an adhesive, particularly in the production of paper and wood adhesives. Its water solubility allows for easy application, and it can form strong bonds when it dries. PVA adhesives are used in products like wood glue, bookbinding adhesives, and school glues. They are favored because they are easy to clean up with water and are generally non-toxic.
- Textile and Paper Industries
In the textile industry, PVA is used as a sizing agent to strengthen and stiffen fibers before weaving or printing. It helps to improve the quality of yarn and fabric by reducing the occurrence of breakage during processing. In the paper industry, PVA is used in coatings, as it can provide a smooth, glossy finish to paper products, making them more attractive and durable.
- Pharmaceuticals
In the pharmaceutical industry, PVA is used in various applications, particularly as a film-forming agent in drug delivery systems. It is used to coat tablets, providing a protective layer and helping to control the release of the drug. PVA is also used in wound dressings, where its ability to form a protective barrier is beneficial for preventing infection and promoting healing.
- Cosmetics
Polyvinyl alcohol is used in some cosmetic formulations, including skin care products, shampoos, and hair conditioners. It acts as a binder, stabilizer, or film-forming agent, enhancing the texture and stability of these products. PVA is also used in nail polish formulations as a thickening agent.
- Biodegradable Products
Given its water solubility and biodegradability, PVA is increasingly being explored as an environmentally friendly alternative to non-biodegradable polymers in the production of biodegradable packaging materials, agricultural films, and other single-use products. These products offer a sustainable solution to reducing plastic waste, as PVA breaks down in natural environments more easily than traditional plastics.
Conclusion
Polyvinyl Alcohol (PVA) is a versatile, water-soluble polymer that finds applications across a wide range of industries. Its chemical structure, characterized by hydroxyl groups, imparts properties such as water solubility, film formation, biodegradability, and adhesive strength. Whether used in packaging, adhesives, textiles, pharmaceuticals, or cosmetics, PVA plays a critical role in many commercial products.