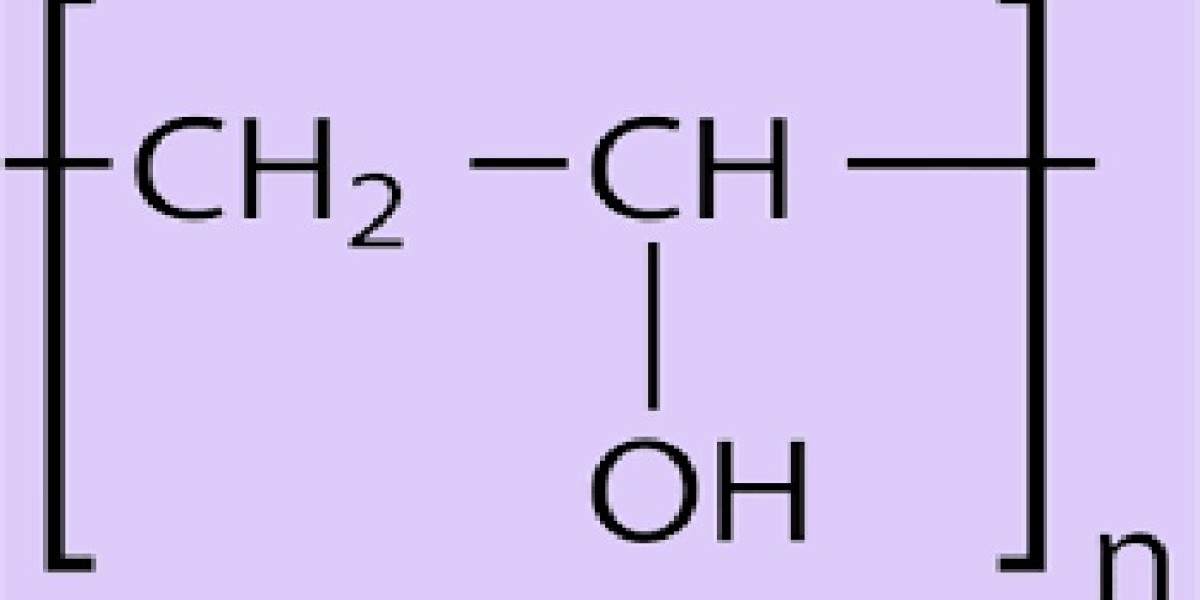
Polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) is a synthetic polymer with numerous applications across a variety of industries. Its chemical structure, properties, and versatility make it an important material in the fields of packaging, textiles, pharmaceuticals, and more. This article explores the production, properties, and uses of polyvinyl alcohol, shedding light on its wide-reaching impact on modern technologies. Polyvinylalkohol
Production and Chemistry of Polyvinyl Alcohol
Polyvinyl alcohol is a water-soluble synthetic polymer, created by the polymerization of vinyl acetate followed by hydrolysis (or saponification). The polymerization process involves the reaction of vinyl acetate monomers, which are polymerized into polyvinyl acetate (PVAc). In the subsequent hydrolysis stage, the ester groups (-COOCH3) in polyvinyl acetate are partially or fully replaced by hydroxyl groups (-OH), resulting in polyvinyl alcohol.
The degree of hydrolysis (the extent to which the ester groups are converted into alcohol groups) and the polymer’s molecular weight play key roles in determining the physical properties of the material. Polyvinyl alcohol can be produced with a wide range of hydrolysis levels, from 85% to 99%, and with varying molecular weights. The higher the degree of hydrolysis, the more crystalline the material, which imparts greater mechanical strength and water resistance. The molecular weight of the polymer affects its viscosity in solution and its ability to form films.
Properties of Polyvinyl Alcohol
Polyvinyl alcohol is known for its impressive range of properties that make it adaptable to different applications. Some of its key characteristics include:
- Water Solubility: Polyvinyl alcohol is highly soluble in water, especially in its low to medium molecular weight forms. This solubility makes it useful in applications where water-based formulations are needed, such as in adhesives, coatings, and films.
- Biodegradability: One of the key benefits of PVA is its biodegradability. The polymer can be broken down by microorganisms under certain environmental conditions, which makes it an attractive alternative to synthetic polymers that take hundreds of years to degrade. This property has spurred interest in using PVA in eco-friendly applications.
- Film-Forming Capabilities: PVA forms clear, flexible, and strong films, which is one reason it is used in packaging materials, as well as in medical and pharmaceutical formulations. Its film-forming ability also makes it a popular choice in applications requiring controlled release mechanisms, such as drug delivery systems.
- Chemical Resistance: Polyvinyl alcohol is resistant to oils, greases, and organic solvents, although it is sensitive to strong acids and bases. This resistance makes it ideal for applications requiring exposure to harsh chemicals.
- High Tensile Strength: Polyvinyl alcohol exhibits high tensile strength, which is important in applications requiring durability and resistance to mechanical stress, such as in certain textile coatings and adhesives.
- Thermal Stability: PVA’s thermal stability varies depending on the degree of hydrolysis and the molecular weight. Generally, the polymer has good thermal stability but begins to decompose at higher temperatures, especially if exposed to heat for extended periods.
- Non-toxicity: Polyvinyl alcohol is non-toxic and generally regarded as safe for use in food contact materials and pharmaceuticals. This property enhances its appeal for a wide range of consumer products.
Applications of Polyvinyl Alcohol
Polyvinyl alcohol’s wide range of beneficial properties makes it suitable for a diverse array of applications, spanning several industries. Some of the most common applications include:
- Packaging: Polyvinyl alcohol is used in the production of biodegradable films and packaging materials. These films are particularly valuable in food packaging, where they serve as protective layers while being environmentally friendly. PVA-based films can be made to dissolve in water, allowing them to be used in products like laundry pods or as edible films for food packaging.
- Textiles: In the textile industry, polyvinyl alcohol is used as a sizing agent for yarns and fabrics, helping to improve their strength and smoothness during the weaving process. PVA is also used in textile finishing processes, such as coating, to impart additional durability and resistance to dirt or moisture.
- Pharmaceuticals: In the pharmaceutical sector, polyvinyl alcohol is used in the formulation of controlled-release drug delivery systems. PVA-based films are used to encase drugs, ensuring that they are released slowly and steadily over time. Additionally, PVA is used in the production of wound dressings and as a binder in tablet formulations.
- Adhesives: Polyvinyl alcohol is used in the production of adhesives due to its excellent adhesive properties. PVA-based adhesives are commonly used in woodworking, paper, and packaging applications. They are especially valued for their ability to bond to porous surfaces.
- Cosmetics: PVA is found in some cosmetic products, including facial masks and hair treatments. Its film-forming ability helps create a smooth, even layer on the skin or hair, and it can contribute to moisture retention or provide a temporary barrier against external contaminants.
- Medical Applications: Polyvinyl alcohol is also utilized in the medical field, particularly in the development of surgical sutures, contact lenses, and various wound care products. Its non-toxicity and ability to form biocompatible materials make it ideal for use in medical devices.
- Electronics: PVA has found uses in the electronics industry, specifically in the manufacturing of lithium-ion batteries and flexible electronics. Polyvinyl alcohol-based materials can be used in the production of separator films and coatings, which play a crucial role in the performance and stability of batteries.
Environmental Impact and Future Prospects
Polyvinyl alcohol is seen as an environmentally friendly material in comparison to many other synthetic polymers due to its biodegradability. As the world increasingly moves toward sustainability, the demand for biodegradable and non-toxic materials like PVA is likely to grow. Additionally, PVA’s solubility in water makes it easier to recycle or dispose of compared to many plastics, which can persist in the environment for years.
There are ongoing efforts to improve the properties of polyvinyl alcohol to make it even more versatile and efficient. Researchers are exploring ways to modify the polymer’s structure to enhance its resistance to degradation in specific applications while maintaining its biodegradability in others. The development of PVA-based nanocomposites and smart materials is also an exciting area of research, offering potential for advanced applications in fields ranging from medicine to environmental remediation.
Conclusion
Polyvinyl alcohol is a highly versatile and valuable polymer that is used in a wide variety of applications. Its unique combination of water solubility, biodegradability, film-forming ability, and non-toxicity makes it a highly sought-after material in many industries, including packaging, textiles, pharmaceuticals, and more. As research into its properties and applications continues to advance, polyvinyl alcohol is poised to play an even more significant role in a wide array of technologies, contributing to both innovation and sustainability in the years to come.