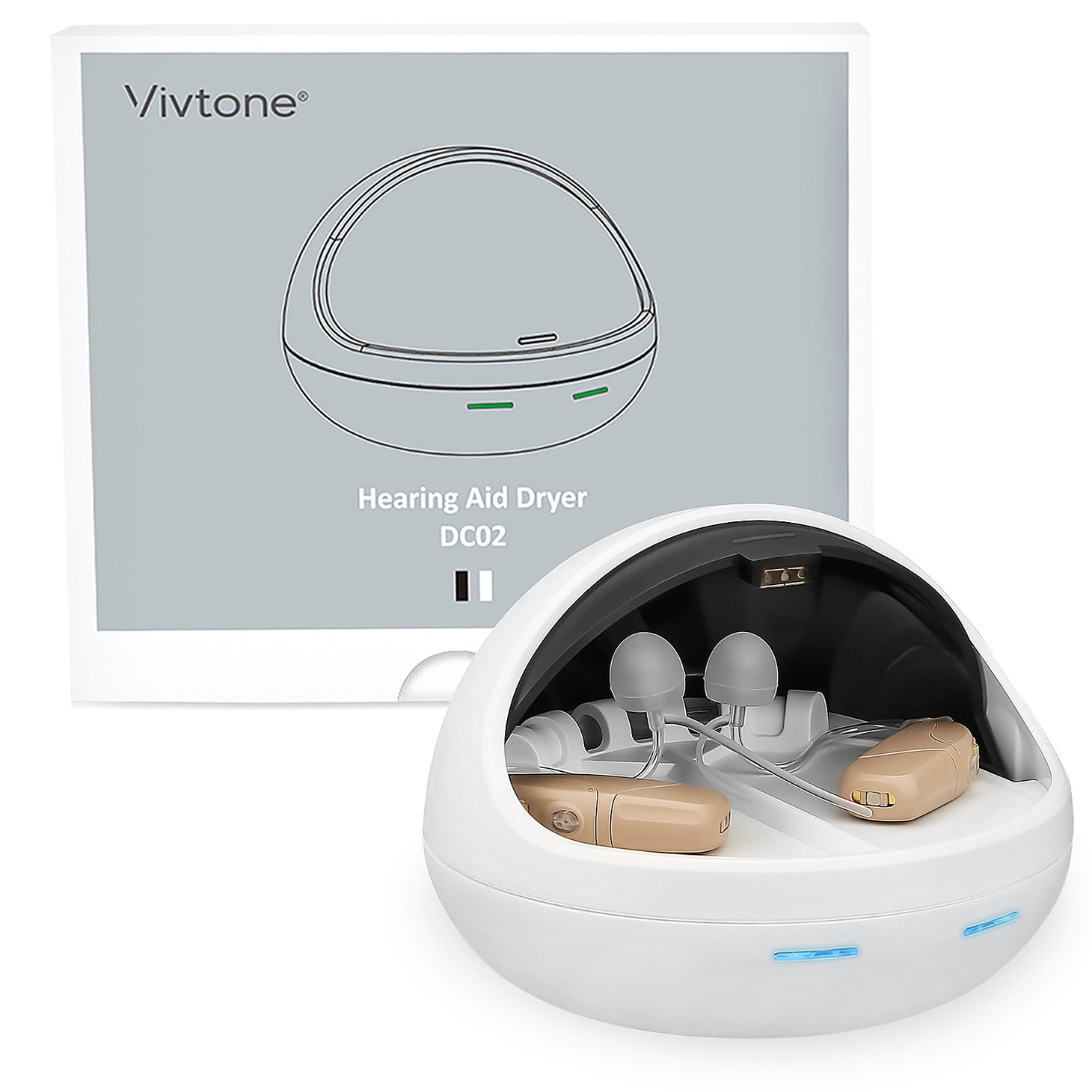
Unlock a World of Sound: Discover Essential Hearing Aid Replacement Parts!
Hearing aids play a vital role in enhancing the quality of life for individuals experiencing hearing loss. They not only help in communication but also enable users to engage fully with their surroundings. However, like any electronic device, hearing aids can face challenges when their components wear out or break. This situation can lead to frustrating experiences, as users may find themselves struggling to hear clearly. Understanding the significance of replacement hearing aid parts is crucial for maintaining optimal hearing experiences. By being informed about these parts and their functions, users can ensure their devices continue to perform at their best, allowing them to unlock a world of sound.
Understanding Hearing Aid Components
Hearing aids consist of several key components that work together to amplify sound and improve the user's auditory experience. The main parts include the microphone, amplifier, receiver, and battery. The microphone captures sound from the environment, converting it into electrical signals. These signals are then sent to the amplifier, which increases their strength. Finally, the receiver converts these amplified signals back into sound waves, which are delivered to the ear. Each component plays a crucial role in the overall performance of the hearing aid, highlighting the importance of understanding how they function and the impact of any potential malfunctions. For instance, when a microphone fails, the device may not pick up sounds effectively, making communication challenging for the user.
Common Replacement Parts for Hearing Aids
Several parts of hearing aids may require replacement over time due to wear and tear. Some of the most commonly replaced components include batteries, ear tips, tubes, and microphones. Batteries are essential for powering the device, and their lifespan can vary based on usage. Ear tips, which create a comfortable fit in the ear, can degrade or become clogged with earwax, affecting sound quality. Tubes can also become brittle or blocked, leading to reduced sound transmission. Additionally, microphones, being sensitive components, can malfunction due to moisture or damage. Recognizing the signs of wear in these parts is important, as their performance directly affects the overall functionality of the hearing aid. A friend of mine recently had to replace her ear tips after experiencing issues with sound clarity; she was amazed at the difference it made in her ability to hear conversations.
Battery Types and Lifespan
Hearing aids typically use either disposable or rechargeable batteries, with each type having its own lifespan and characteristics. Disposable batteries usually last anywhere from three to ten days, depending on usage and the specific device model. Users can often gauge when a battery needs replacing by monitoring the sound quality and volume – a decrease in either can indicate a low battery. Rechargeable batteries, on the other hand, generally provide a longer-lasting solution, but they also require regular charging to maintain optimal performance. It's crucial for users to understand the type of battery their hearing aid uses and to establish a routine for checking battery life to avoid unexpected interruptions in their hearing experience.
Where to Find Replacement Parts
When it comes to purchasing replacement parts for hearing aids, users have several options. Online retailers provide a convenient platform for finding various components, often offering a wider selection than local stores. However, it's essential to ensure that the parts are compatible with the specific hearing aid model. Local audiology clinics and hearing aid specialists can also be excellent resources, as they often stock high-quality parts and can provide expert advice on what is needed. Visiting a specialist can be particularly beneficial for those uncertain about compatibility or quality, ensuring that any purchased parts will enhance the functionality of their devices.
Tips for Maintaining Hearing Aids
Proper maintenance of hearing aids is crucial for prolonging their lifespan and ensuring consistent performance. Regular cleaning is essential; users should follow a routine that includes wiping down the exterior with a soft cloth and using a brush to remove any debris from the microphone and receiver. Additionally, storing hearing aids in a dry, cool place when not in use can help prevent moisture damage. It's also advisable to have the devices checked periodically by a professional to ensure that all components are functioning correctly. By taking these proactive measures, users can maintain their hearing aids in optimal condition and enjoy a better hearing experience.
Importance of Replacement Hearing Aid Parts
In conclusion, understanding the key replacement parts for hearing aids is crucial for ensuring that these devices continue to function effectively. From batteries to microphones, each component plays a significant role in the overall performance of hearing aids. By being proactive in replacing worn or damaged parts and maintaining their devices through regular cleaning and professional checks, users can greatly enhance their hearing experiences. The journey to better hearing is ongoing, and being informed about replacement parts is an essential part of that journey.